Imagine a world where money moves across borders in seconds without banks, where supply chains can be tracked with total transparency, and where contracts execute themselves automatically without lawyers. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the power of blockchain technology.
Since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009, blockchain has evolved from the backbone of cryptocurrencies into one of the most disruptive technologies of our time. Today, it’s reshaping industries from finance to healthcare, supply chains to voting systems, offering a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to record and share information.
But what exactly is blockchain? How does it work under the hood? And why is it considered such a breakthrough?
In this guide, we’ll break blockchain down step by step, covering the core concepts, mechanics, benefits, and real-world use cases, so by the end, you’ll have a crystal-clear understanding of why blockchain matters in 2025 and how it works in practice.
Understanding Blockchain: Beyond the Buzzword
At its most basic, a blockchain is a digital ledger, a record of transactions. But unlike traditional ledgers that are controlled by banks or corporations, blockchain is distributed across thousands of computers, known as nodes, around the world.
Every node holds a copy of the ledger, which means no single party can alter the records without everyone noticing. This decentralization removes the need for intermediaries and makes blockchain highly transparent and tamper-resistant.
A blockchain has three defining characteristics:
- Decentralization: Instead of a single authority, many participants maintain and verify the system.
- Immutability: Once data is added, it cannot be deleted or altered.
- Transparency: Anyone can view transactions on public blockchains.
Think of blockchain as a community-owned notebook. Every time someone writes an entry (a transaction), everyone in the community gets an updated copy. Once written, no one can erase it, only add new entries.
How Blockchain Works: Step by Step
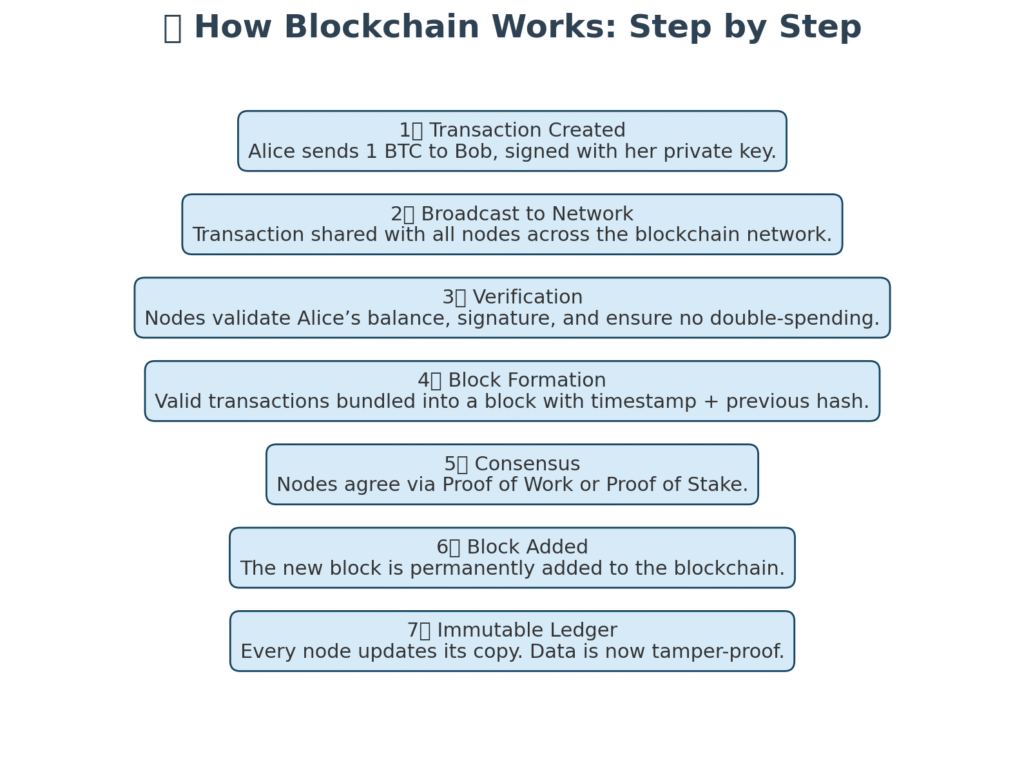
To truly understand blockchain, let’s walk through the process of a simple transaction, such as Alice sending Bitcoin to Bob.
Step 1: Transaction Creation
Alice initiates a transaction, specifying the amount of Bitcoin and Bob’s wallet address. This transaction is digitally signed with Alice’s private key, ensuring authenticity.
Step 2: Broadcasting to the Network
The transaction is sent to the blockchain’s peer-to-peer network, where it is visible to all participating nodes.
Step 3: Verification by Nodes
Nodes validate the transaction by checking:
- Does Alice have enough Bitcoin to send?
- Has she tried to double-spend the same coin?
- Is the digital signature valid?
Only valid transactions move forward.
Step 4: Formation of a Block
Validated transactions are bundled together into a new block. Each block contains:
- The list of verified transactions
- A timestamp
- A unique cryptographic hash of the previous block
This hash links the new block to the old one, ensuring continuity.
Step 5: Consensus Mechanism
Before adding the block to the chain, the network must agree it’s valid. This is done through consensus mechanisms like:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve mathematical puzzles to add blocks (used by Bitcoin).
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the tokens they stake (used by Ethereum).
Step 6: Block Added to the Chain
Once consensus is reached, the block is permanently added to the blockchain. Every node updates its copy, ensuring everyone has the same record.
Step 7: Immutability and Transparency
From this point, altering Alice’s transaction would require rewriting every block after it across the entire network, an almost impossible task.
Why Blockchain Matters
Blockchain solves the problem of trust in digital systems. Traditionally, we rely on third parties (banks, governments, clearinghouses) to verify and record transactions. Blockchain removes this dependency by allowing the network itself to validate activity.
Key Benefits
- Trustless Transactions: No need to rely on middlemen.
- Security: Data is cryptographically secured and decentralized.
- Transparency: All participants can see the history of transactions.
- Efficiency: Transactions can be processed faster and at lower cost.
This combination of qualities is why blockchain is often called the Internet of Value.
Types of Blockchain
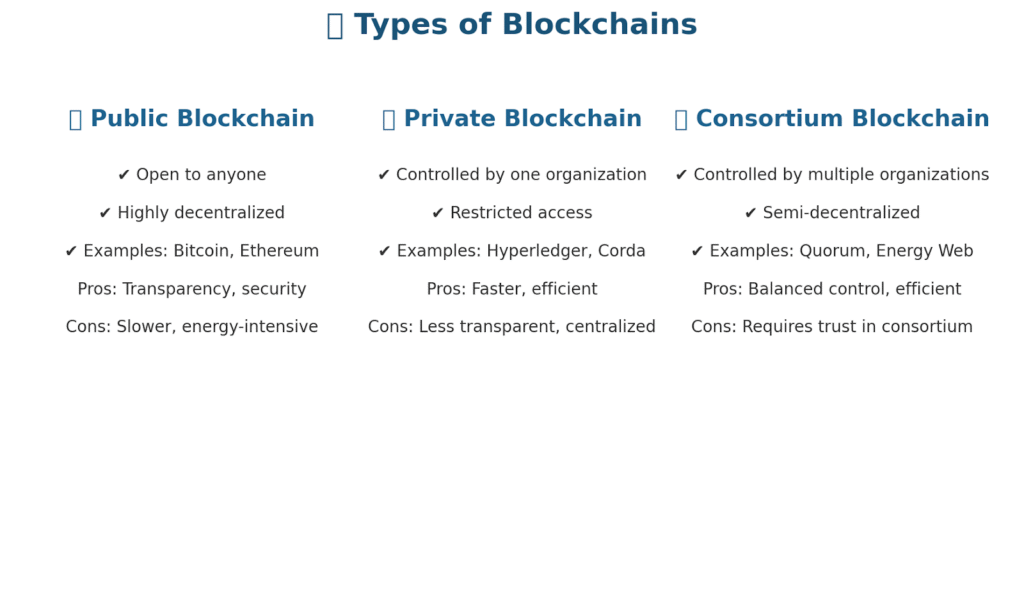
There isn’t just one kind of blockchain. Different industries use different models depending on their needs.
1. Public Blockchains
- Open to anyone (Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Completely decentralized.
- Best for transparency and security.
2. Private Blockchains
- Controlled by one organization.
- Access restricted to invited participants.
- Faster but less decentralized.
3. Consortium Blockchains
- Managed by a group of organizations.
- Balance between efficiency and decentralization.
- Common in industries like banking or logistics.
Consensus Mechanisms: The Heart of Blockchain
Consensus ensures that all participants in the network agree on the state of the ledger. Without it, there would be chaos.
Proof of Work (PoW)
- Used by Bitcoin.
- Miners compete to solve complex puzzles.
- Very secure but consumes large amounts of energy.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Validators are chosen based on how many tokens they “stake.”
- More energy-efficient and faster than PoW.
- Adopted by Ethereum after its 2022 “Merge.”
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Token holders vote to elect a small number of validators.
- Faster but more centralized.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain is no longer limited to cryptocurrency. It’s already transforming industries worldwide.
- Finance: Enables instant cross-border payments without banks.
- Supply Chain: Tracks products from origin to customer with transparency.
- Healthcare: Stores medical records securely and privately.
- Voting: Creates tamper-proof voting systems.
- Smart Contracts: Programs on blockchains that execute automatically when conditions are met.
- Digital Identity: Allows individuals to control and verify their identity securely.
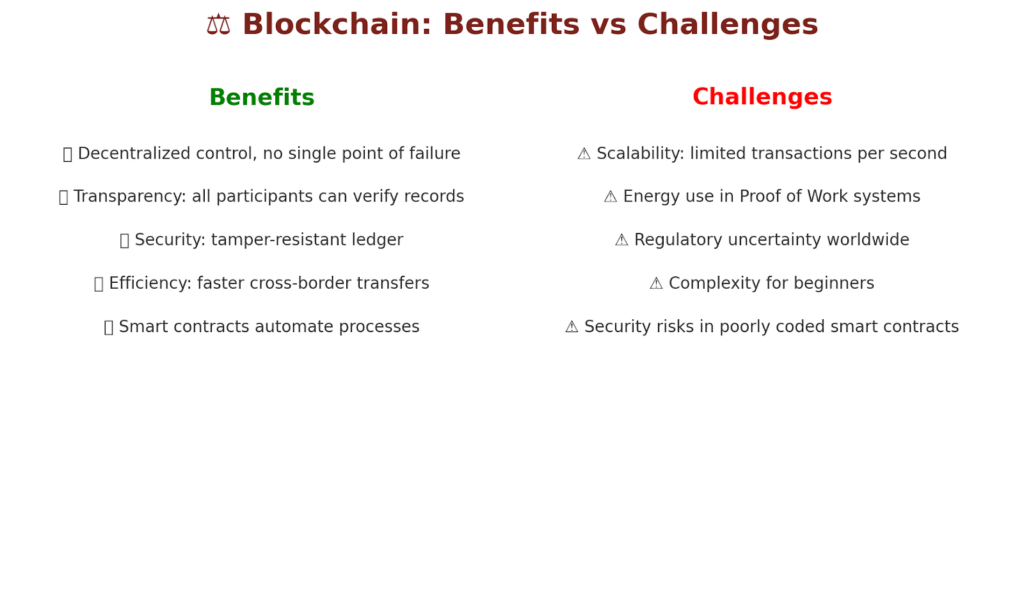
Advantages of Blockchain
- Decentralized Control: No single point of failure.
- Tamper-Proof Records: Immutability ensures integrity.
- Transparency for All: Builds trust between participants.
- Automation: Smart contracts streamline processes.
Challenges Facing Blockchain
While powerful, blockchain is not without challenges:
- Scalability: Current blockchains process fewer transactions per second than centralized systems.
- Energy Use: PoW networks consume enormous electricity.
- Regulation: Governments are still catching up with blockchain laws.
- Complexity: The technology has a steep learning curve for beginners.
Blockchain is more than the foundation of cryptocurrencies; it is a transformative technology reshaping how we handle trust, data, and value. Its decentralized, immutable, and transparent nature makes it one of the most important inventions of the 21st century.
As adoption grows, blockchain will continue to find new applications in everyday life, from financial systems to healthcare, supply chains, and governance. Understanding how it works is essential for anyone who wants to participate in the digital economy of the future.
By breaking free from centralized control, blockchain gives us a glimpse into a world where individuals, not institutions, hold the power.
Read also: Qubic Network Targets Dogecoin After Monero Attack
